The transcriptome comprises all RNAs present in a specific cell or tissue type at a distinct time. Their presence and abundance correspond to the current metabolic state of the cells and are affected by external and internal changes. Transcriptome sequencing is a powerful method to detect and quantify RNA molecules.
Application areas and objectives for transcriptome sequencing are diverse and include
- the analysis of differential gene expression levels, and
- the detection of alternative splicing and previously unknown transcripts.
We offer various Transcriptome Sequencing products that provide reliable and accurate insights into the RNA present in a specific cell or tissue type at a distinct time.
CeGaT Is the Best Partner for Sequencing Your Project
Our Commitment to You
Fast Processing
Turnaround time
≤ 15 business days
High Quality
Highest accuracy for all processes
Secure Delivery
Secure provision of sequenced data via in-house servers
Safe Storage
Safe storage of samples and data after project completion
Our Service
We provide a comprehensive and first-class project support – from selecting the appropriate product to evaluating the data. Each project is supervised by a committed scientist. You will have a contact person throughout the whole project.
Our service includes:
- detailed project consulting
- product selection tailored to your project
- detailed bioinformatic evaluation of your data
- detailed project report with information about sample quality, sequencing parameters, bioinformatic analysis, and results
Benefit from our dedicated support and accredited workflows.
Explore Our Product Portfolio for Transcriptome Sequencing
We offer Whole Transcriptome Sequencing (WTS), Coding Transcriptome Sequencing (CTS), and Flexible Solutions (TS) to address a variety of research questions. Would you like to have bioinformatic analyses performed on your data in addition to the included deliverables? Each of our products can be supplemented with further services. We are happy to advise you.
CTS Classic | WTS Classic | WTS Classic Deep | TS Flex |
Species | Species | Species | Species |
RNA quality & input | RNA quality & input | RNA quality & input | RNA quality & input |
RNA Target | RNA Target | RNA Target | RNA Target |
Sequencing platform | Sequencing platform | Sequencing platform | Sequencing platform |
Output | Output | Output | Output |
Included deliverables | Included deliverables | Included deliverables | Included deliverables |
Bioinformatics
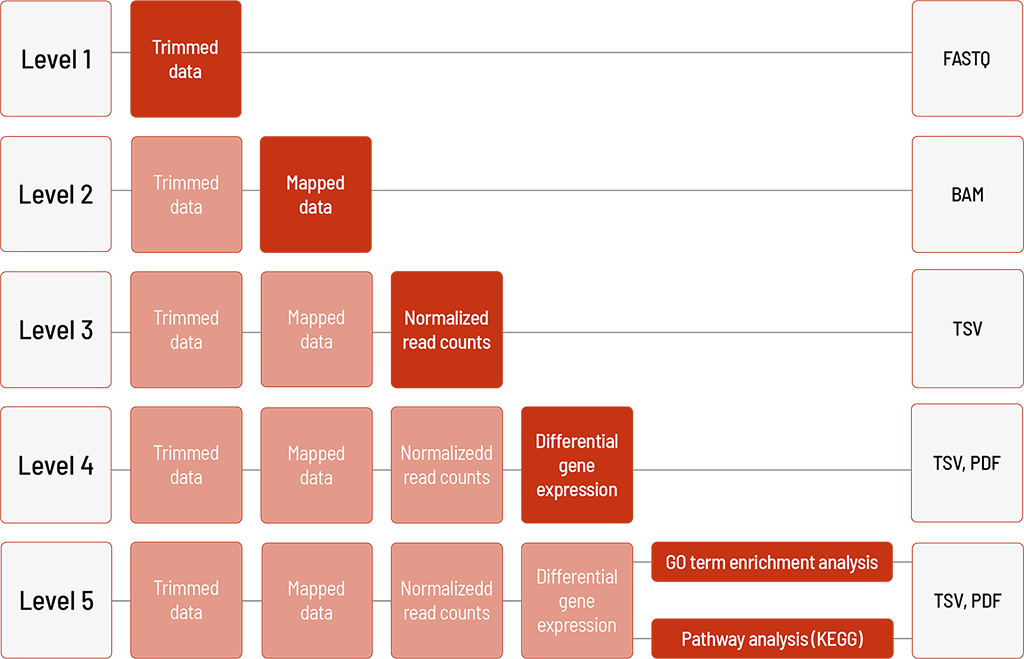
Raw sequencing data are automatically processed. We offer different levels of bioinformatic analysis. The default level is Level 1. With increasing bioinformatic level, more data are delivered. All higher levels include the data from the lower levels. In addition to the data, and independent of the analysis level, a project report is generated.
Level 1:
- demultiplexing and adapter trimming of the sequencing data (FASTQ format)
Level 2:
- mapping and deduplication of the sequencing data (BAM format)
Level 3:
- normalization of read counts (TSV format)
Level 4:
- group comparison and differential gene expression analysis (TSV format)
- visualization in heat map, MA plot, and volcano plot (PDF format)
⚠ For the differential gene expression analysis (group comparison), a minimum of three replicates per group is required.
Level 5 (one of the following)
- GO term enrichment analysis (TSV and PDF format)
– for human samples and selected organisms - Pathway analysis (KEGG) (TSV and PDF format)
– for human samples and selected organisms
Technical Information
At CeGaT, paired-end sequencing (2 x 100 bp) is performed using Illumina sequencing platforms. If you require other sequencing parameters, please let us know!
We can provide further solutions.
Further Information on Transcriptome Sequencing
Transcriptome sequencing is also known as RNA Sequencing (RNA seq). Using this approach, the present RNA molecules are analyzed at a certain time point within a sample. Thus, the metabolic state of a certain sample at a distinct time is displayed and reflects the biological state of the cells. Transcriptome sequencing enables the identification of alternative genes, spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, gene fusions, and changes in gene expression over time, over treatment or between different groups. Thus, with transcriptome sequencing, gene function and gene structure can be interpreted. Furthermore, the function of non-protein coding RNAs can be analyzed. Transcriptome sequencing can reveal molecular mechanisms of disease occurrence and specific biological processes. Additionally, rare or unknown transcripts can be identified, as well as variable cleavage sites and coding sequence single nucleotide polymorphisms.
RNA seq has advantages over other transcriptomic technologies, such as microarrays. It is highly sensitive, allowing for the detection and quantification of almost all transcripts in the cell. Additionally, RNA seq accurately determines each single nucleotide of every transcript. In contrast to, for example, microarray technologies, RNA seq has no difficulties with cross-reactions or background noise from fluorescence signals.
Within RNA seq, different approaches can be used. It is possible to either analyze the whole transcriptome or the coding transcriptome. With whole transcriptome sequencing, coding RNA as well as many types of non-coding RNAs are covered. In contrast, coding transcriptome sequencing targets the mRNA molecules. Its main objective is the quantification of gene expression and the differential gene expression analysis.
Thus, depending on the experimental setup or research objective, total RNA or messenger RNA can be sequenced. Total RNA comprises both – coding and non-coding RNA. We call this product WTS, for Whole Transcriptome Sequencing. The RNA isolation can be done from cells, blood, or even from FFPE embedded tissue. It can be done either by you or by CeGaT. Total RNA contains many different types of RNA, such as messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and non-coding RNA.
After reverse transcription, the addition of adapters and barcodes, and the PCR amplification step, the final library is sequenced on one of our state-of-the-art sequencing instruments. Even challenging samples, such as fragmented RNA, perform well with our total RNA protocols. Since ribosomal RNA comprises more than 80% of all cellular RNAs, we recommend rRNA depletion. We can analyze the transcriptome of mammals, plants, viruses, and bacteria, and we have established many different total RNA protocols for all kinds of applications. The whole transcriptome analysis enables a comprehensive and genome-wide overview of all transcripts in an organism, and genome-wide expression analysis. You can analyze introns, exons, but also regions in between to shed light into splicing mechanisms.
Sequencing of the coding RNA is the most common transcriptome sequencing approach. We call this product CTS, for Coding Transcriptome Sequencing. The messenger RNA has a coding region, which is flanked by two UTRs, so-called untranslated regions, at the 5’ and 3’ end. It carries a 5’ cap and a poly adenylation, the so-called poly-A tail, at the 3’ end. This poly-A tail enhances the stability and the translation efficiency of the mRNA. Most eukaryotes carry this poly-A tail, such as mammals, insects, plants, fungi, and fish. However, it is not present in the mRNA of bacteria. This poly-A tail is essential for the mRNA library preparation. mRNA constitutes only 1-5% of the total RNA. Once the RNA has been isolated from cells or from tissue, the mRNA needs to be purified, using poly-T oligos, which are attached to magnetic beads, and which bind to the poly-A tail. And again, the final sequencing library is then analyzed on one of our modern sequencing instruments.
We can analyze the coding transcriptome of mammals, plants, and other eukaryotes. mRNA sequencing is very sensitive, especially, if you want to analyze mRNA, which is only expressed at very low levels. The main objective of mRNA sequencing is the quantification of gene expression and differential gene expression analysis. It is often used to analyze gene expression levels between different groups, especially when you are planning drug treatment- or disease-related experiments.
Downloads
Contact Us
Do you have a question or are you interested in our service? Feel free to contact us. We will take care of your request as soon as possible.
Start Your Project with Us
We are happy to discuss sequencing options and to find a solution specifically tailored to your clinical study or research project.
When getting in contact, please specify sample information including starting material, number of samples, preferred library preparation option, preferred sequencing depth and required bioinformatic analysis level, if possible.