One of the effects of demographic change is that people are getting older on average. As a result, diseases that typically occur later in life are becoming more common. Age is a decisive factor in dementia. However, genetic factors also play a role, which can lead to an increased risk and an early onset of the disease.
We can help you to identify potential genetic risk factors. A genetic analysis of risk factors can give those seeking advice clarity about how high the individual genetic risk of dementia is. This means that you are prepared in the event of illness.
Are you insured in Germany? Our colleagues at Zentrum für Humangenetik Tübingen will gladly support you!
The Advantages of Our Predictive Dementia Analysis
What is Dementia?
Dementia is a pattern of symptoms that can be attributed to different diseases and causes. One of these causes is Alzheimer’s disease. Dementia is characterized by the progressive loss of memory, language, sense of direction, and other thinking processes. Regardless of the cause of dementia, the symptoms are caused by the loss of nerve cells.
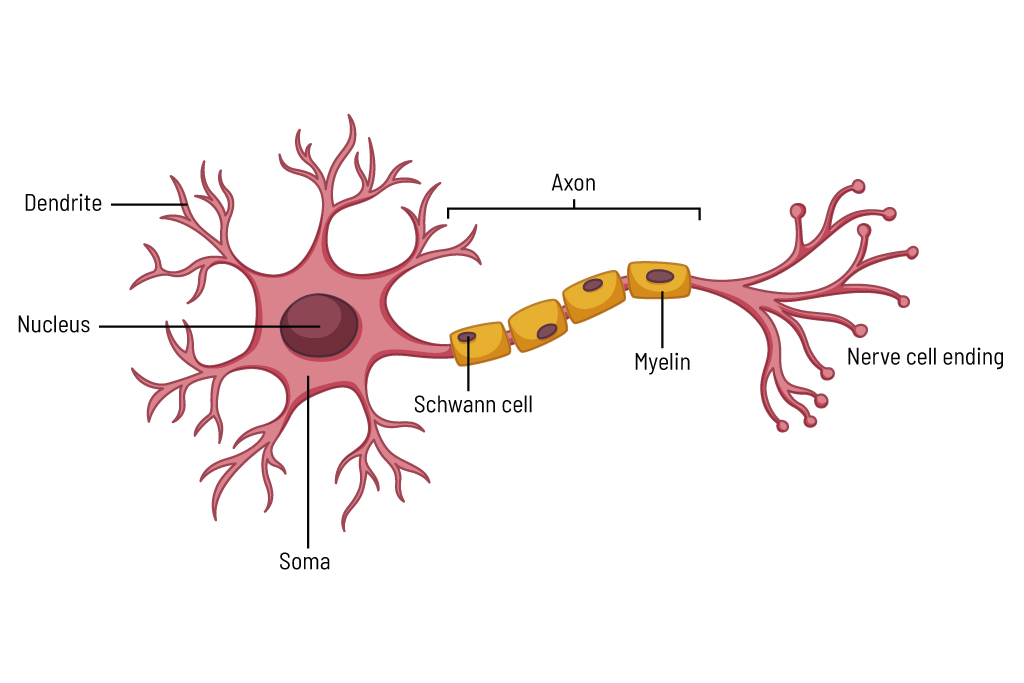
Nerve cells are responsible for transmitting signals in the brain. They contain a cell body (soma) with a cell nucleus. A signal arrives at the dendrites (branch-like extensions on the cell body of the nerve cell). The signal is processed in the cell body and transmitted via an axon (long cell extension) to the next cell. A special layer surrounds this conductive cell extension, the myelin sheath of Schwann cells, which enables the electrical signals to be transmitted more quickly. At the nerve endings, the signal is then transmitted to the next cell with the help of chemical or electrical signals (figure 1). This enables information to be passed on in the brain and thinking processes to be carried out. If damage to the nerve cells occurs, these processes can be impaired and lead, e.g., to memory loss.
The loss of nerve cells can, e.g., be triggered by age-related changes in the structure of the nerve cells, or it can be a consequence of other diseases. Genetics can also influence when and how the disease occurs.
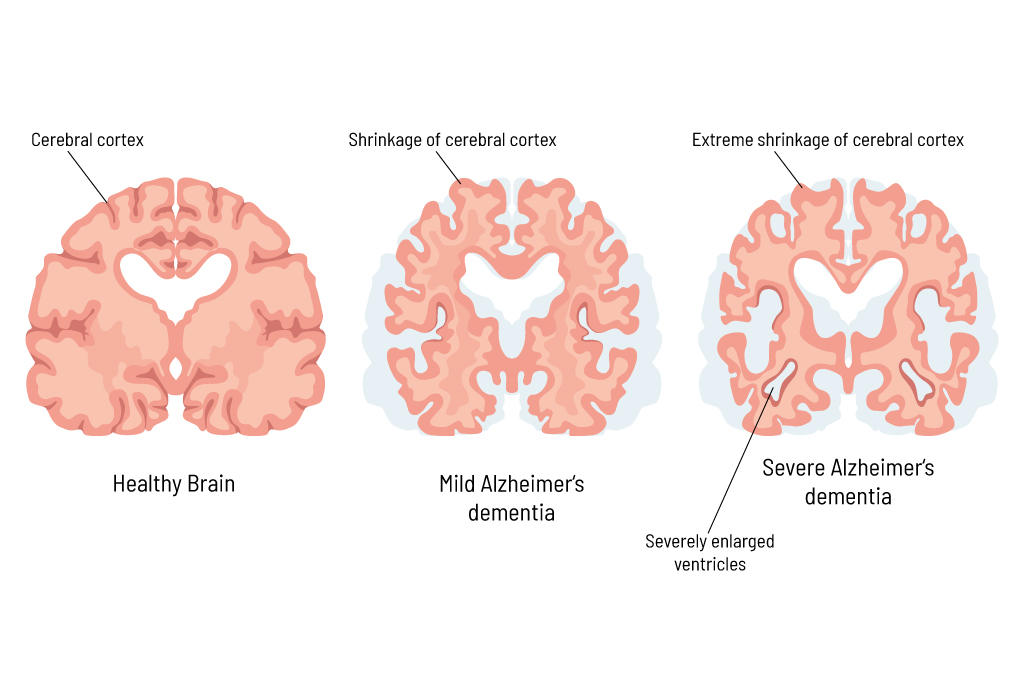
Damage to the neurons occurs, e.g., due to incorrectly processed proteins. These proteins form deposits and damage the nerve cells. An undersupply of nutrients can also be the cause of damage to the neurons. As a result, the symptoms described above can occur. The loss of many nerve cells can also be recognized by the change in brain structure (figure 2).
Field Report
Annika M., 41 years old
Lifestyle: regularly walks her dog
Result: our predictive diagnostics identified a variant in the APP gene in Annika M. that leads to an increased risk of dementia.
Consequence: Annika M. is sensitized to the topic of dementia and adapts her life planning to the circumstances.
“Thanks to the genetic analysis of predispositions to dementia, I now have certainty and feel prepared.”
How Does Genetic Risk Assessment Work?
Various factors contribute to the development of dementia. We help you determine your genetic risk for this and reliably detect known genetic variants. In the predictive dementia analysis, nine genes associated with a hereditary, increased risk of dementia are tested.
Our Expert
General Information
Genetic Counseling
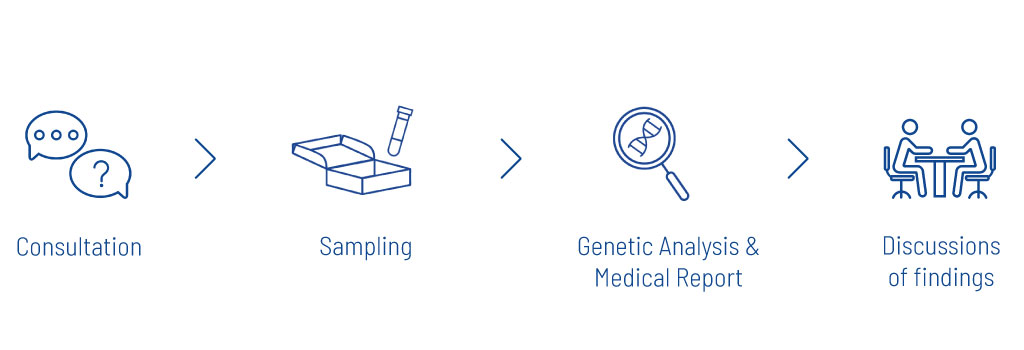
Our genetic counseling provides detailed information to those seeking advice about their genetic testing options and further procedures. During the consultation, we also discuss which genes can be analyzed. We want to ensure that all relevant questions are answered and that people seeking advice can make informed decisions about their health.
Genetic Analysis and Result
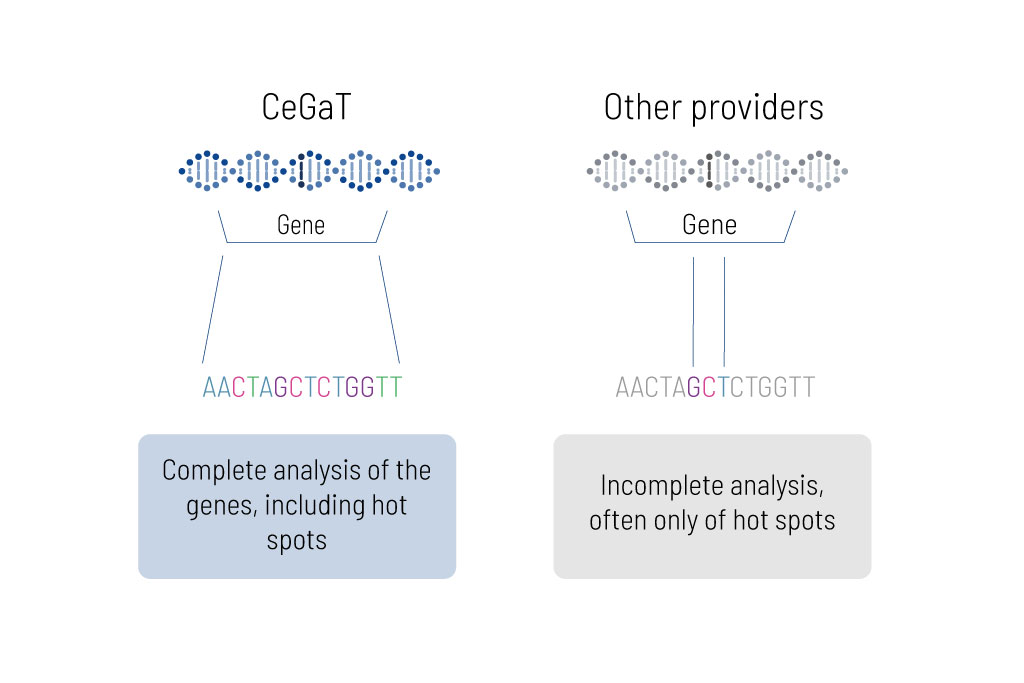
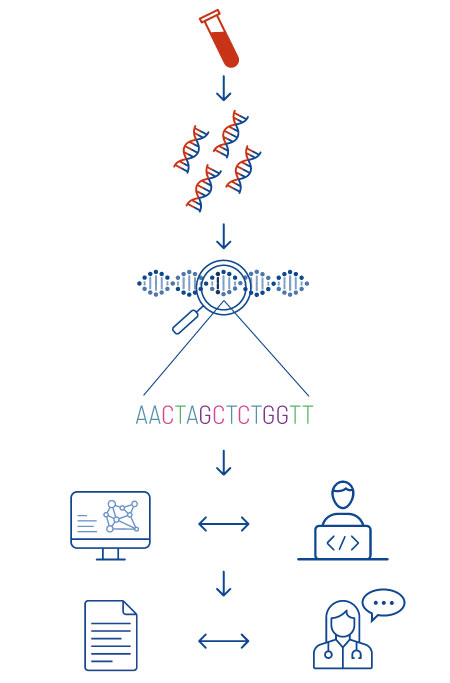
Our in-house laboratory analyzes the genes using an advanced technology called next-generation sequencing, or NGS for short. To do this, we isolate the DNA from the cells in the blood sample (figure 4) and then read the individual building plan of the DNA step by step (sequencing). We do not limit ourselves to so-called hotspot regions. Instead, we read the genes in their entirety.
The sequenced information is then analyzed in-house. We investigate whether particular characteristics or changes (variants) in the genes are associated with an increased risk of disease and play a role in individual health care. We compile the results in a report and conclude by explaining what significance this could have for the health of the person seeking advice.
Further details on sample material and shipment can be found here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Before Choosing a Test
Sample & Analysis
Result & Consultation
Storage and Data Protection
Predictive Healthcare for Companies
Companies and healthcare facilities rely on our many years of experience and expertise in genetic diagnostics.
Are you also interested in predictive healthcare for your employees?
Downloads
Contact Us
Do you have a question, or are you interested in our service?
Diagnostic Support
We will assist you in selecting the diagnostic strategy – whether as a person seeking advice or as a physician.