The changing paradigm – away from a one-size-fits-all approach towards precision medicine – raises the importance of comprehensive genomic profiling of tumor samples. Comprehensive genomic tumor profiling refers to the simultaneous evaluation of several biomarkers within one analysis, together with the detection of somatic mutations. This approach enables detecting the most relevant predictive markers for current targeted therapies and key immuno-oncology biomarkers, such as tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability (MSI). TMB is a biomarker that measures the number of somatic mutations present in a cancer patient’s tumor and is quantified as mutations per megabase (mut/Mb). Another key immunotherapy biomarker is the MSI, which is caused by the failure of the DNA mismatch repair system.
The application areas of comprehensive tumor profiling are manifold, with a focus on:
- stratifying patients for the best treatment choice
- identifying patients eligible for clinical trials
- driving clinical research, especially in the area of immunotherapy
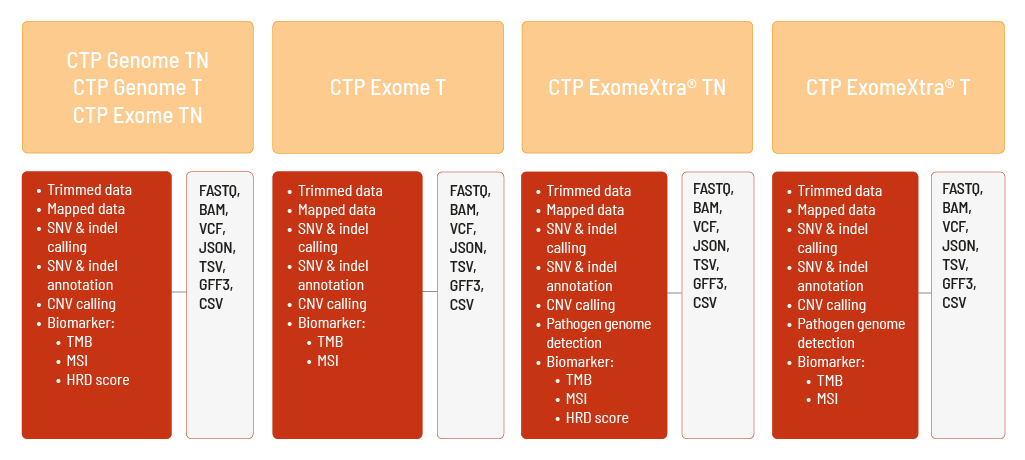
You can choose between different products to perform comprehensive tumor profiling.
CeGaT Is the Best Partner for Sequencing Your Project
Our Commitment to You
Fast Processing
Turnaround time
≤ 15 business days
High Quality
Highest accuracy for all processes
Secure Delivery
Secure provision of sequenced data via in-house servers
Safe Storage
Safe storage of samples and data after project completion
Our Service
We provide a comprehensive and first-class project support – from selecting the appropriate product to evaluating the data. Each project is supervised by a committed scientist. You will have a contact person throughout the whole project.
Our service includes:
- detailed project consulting
- product selection tailored to your project
- detailed bioinformatic evaluation of your data
- detailed project report with information about sample quality, sequencing parameters, bioinformatic analysis, and results
Benefit from our dedicated support and accredited workflows.
Explore Our Product Portfolio for Comprehensive Tumor Profiling
We offer different Comprehensive Tumor Profiling (CTP) products to address a variety of research questions.
If you are interested in sequencing the whole genome of a tumor sample, our Whole Genome Sequencing CTP products give you the most comprehensive insights. For CTP Genome TN, a tumor and a normal sample are used for a tumor-normal comparison. With CTP Genome T, a single tumor sample is analyzed.
Our ExomeXtra® Sequencing products take exome sequencing to the next level. The advantages of our ExomeXtra® Sequencing can also be exploited for tumor samples. CTP ExomeXtra® TN uses a tumor and a normal sample for a tumor-normal comparison. With CTP ExomeXtra® T, a single tumor sample is analyzed.
If you are interested in the exome of a tumor sample, our Whole Exome Sequencing CTP products offer insights into the known coding exons of the human genome. For CTP Exome TN, a tumor and a normal sample are used to perform a tumor-normal comparison. With CTP Exome T, a single tumor sample can be analyzed.
Each of our products can be supplemented with further services. We are happy to advise you.
Whole Genome Sequencing CTP
CTP Genome TN | CTP Genome T |
Species | Species |
Sequencing panel Whole genome | Sequencing panel Whole genome |
Analysis of tumor and normal tissue Yes | Analysis of tumor and normal tissue No |
Starting material Fresh frozen tissue, FFPE tissue, high molecular weight DNA, or fragmented DNA (FFPE) | Starting material Fresh frozen tissue, FFPE tissue, high molecular weight DNA, or fragmented DNA (FFPE) |
Sequencing platform | Sequencing platform |
Output 90 Gb normal tissue 90 Gb tumor tissue | Output 90 Gb tumor tissue |
Included deliverables Project report, files in FASTQ, BAM, CSV, VCF, JSON, GFF3, and TSV format | Included deliverables Project report, files in FASTQ, BAM, CSV, VCF, JSON, GFF3, and TSV format |
ExomeXtra® Sequencing CTP
CTP ExomeXtra® TN | CTP ExomeXtra® T |
Species | Species |
Sequencing panel ExomeXtra® | Sequencing panel ExomeXtra® |
Analysis of tumor and normal tissue Yes | Analysis of tumor and normal tissue No |
Starting material Fresh frozen tissue, FFPE tissue, high molecular weight DNA, or fragmented DNA (FFPE) | Starting material Fresh frozen tissue, FFPE tissue, high molecular weight DNA, or fragmented DNA (FFPE) |
Sequencing platform | Sequencing platform |
Output 18 Gb normal tissue 24 Gb tumor tissue | Output 24 Gb tumor tissue |
Included deliverables Project report, files in FASTQ, BAM, CSV, VCF, JSON, GFF3, and TSV format | Included deliverables Project report, files in FASTQ, BAM, CSV, VCF, JSON, GFF3, and TSV format |
Whole Exome Sequencing CTP
CTP Exome TN | CTP Exome T |
Species | Species |
Sequencing panel Whole exome | Sequencing panel Whole exome |
Analysis of tumor and normal tissue Yes | Analysis of tumor and normal tissue No |
Starting material Fresh frozen tissue, FFPE tissue, high molecular weight DNA, or fragmented DNA (FFPE) | Starting material Fresh frozen tissue, FFPE tissue, high molecular weight DNA, or fragmented DNA (FFPE) |
Sequencing platform | Sequencing platform |
Output 12 Gb normal tissue 24 Gb tumor tissue | Output 24 Gb tumor tissue |
Included deliverables Project report, files in FASTQ, BAM, CSV, VCF, JSON, GFF3, and TSV format | Included deliverables Project report, files in FASTQ, BAM, CSV, VCF, JSON, GFF3, and TSV format |
If you are interested in more focused analyses of tumor samples using gene panels, please check out our Focused Tumor Profiling product portfolio.
Bioinformatics
Raw sequencing data are automatically processed. We analyze your Comprehensive Tumor Profiling data with the DRAGEN Bio-IT Platform. We can perform the analyses based on the human references hg19 and GRCh38. The analysis includes
- demultiplexing and adapter trimming of the sequencing data (FASTQ format),
- mapping of the sequencing data (BAM format),
- calling of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions and deletions (indels) of both germline and somatic variants (VCF format),
- annotation of the SNVs and indels (JSON and TSV format),
- calling of copy number variations (CNVs) (VCF and GFF3 format),
- determination of the biomarkers tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability (MSI) (TSV format).
The HRD score is additionally calculated (CSV format) for CTP Genome TN, CTP Genome T, CTP ExomeXtra® TN, and CTP Exome TN.
Furthermore, for CTP ExomeXtra® TN and CTP ExomeXtra® T, selected pathogen genomes can be detected (TSV format).
Supplementing the data, a project report (PDF format), metrics files (CSV format), and a MultiQC report (HTML format) are provided.
Technical Information
At CeGaT, paired-end sequencing (2 x 100 bp) is performed using the Illumina sequencing platforms. If you require other sequencing parameters, please let us know! We can provide further solutions.
Further Information About Comprehensive Tumor Profiling
The tumor mutational burden, also known as TMB, is the amount of gene mutations occurring in a patient’s tumor but not occurring in the patient’s healthy tissue. Thus, these mutations are coding, somatic mutations. The tumor mutational burden is defined as mutations per megabase (mut/Mb). It should not be confused with the variant allele frequency that only indicates the frequency of an allele. In contrast, the tumor mutational burden is the total amount of mutations per megabase in a sample. Depending on the tumor entity, the tumor mutational burden varies: Some tumors do not show high mutation rates, such as Ewing sarcoma or acute myeloid leukemia. Other cancer types, such as melanomas or lung squamous cell carcinomas, hold a high tumor mutational burden. Thus, the tumor can be classified as low, intermediate, or highly mutated using the tumor mutational burden. The tumor mutational burden is a promising predictive immunotherapeutic biomarker, for example, in immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Such an immunotherapy is especially effective in patients with a high tumor mutational burden. A higher number of tumor-specific mutations leads to a higher number of altered proteins, so-called neoantigens. These neoantigens are different from the healthy proteins, resulting in an increased difference of the tumor tissue compared to the healthy tissue.
Both tumor and healthy cells present parts of their protein content on their cell surface. These presented protein parts are also called peptides. Immune cells regularly check the peptides on the surfaces of the proteins. If the peptides are recognized as foreign, the immune system is activated. The tumor peptides, the neoantigens, are foreign to the immune system. Thus, a higher tumor mutational burden correlates with more mutations and more neoantigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system. With a higher tumor mutational burden, the immune system is activated more easily.
Another immunotherapeutic biomarker is microsatellite instability, also known as MSI. The microsatellite instability indicates the number of mutations in satellite regions. These satellite regions are special DNA repeat sequences. The satellite regions of the DNA are the main component of the functional centromeres, forming the main structure of the heterochromatin. A disturbed DNA mismatch repair mechanisms (MMR) can lead to genetic hypermutability in the satellite regions, resulting in microsatellite instability. The microsatellite instability is classified as stable for a low MSI score or unstable for a high MSI score.
Cells with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) are characterized by a dysfunctional homologous recombination (HR) pathway, which can play a crucial role in carcinogenesis and tumor progression. A tumor cell’s HRD status can have pivotal implications for treatment options, as HRD-positive tumors are sensitive to PARP inhibitors. Thus, assessing a tumor’s HR status can be crucial in the treatment decision.
Downloads
Contact Us
Do you have a question or are you interested in our service? Feel free to contact us. We will take care of your request as soon as possible.
Start Your Project with Us
We are happy to discuss sequencing options and to find a solution specifically tailored to your clinical study or research project.
When getting in contact, please specify sample information including starting material, number of samples, preferred library preparation option, preferred sequencing depth and required bioinformatic analysis level, if possible.