Array CGH, also known as microarray analysis, represents a powerful methodological advancement of classical cytogenetics. Array CGH is used to detect losses or gains of genomic regions in chromosomal material and thus to diagnose unclear dysmorphic, retardation, and malformation syndromes. Compared to conventional chromosome analysis, where the detection limit is 5 to 10 Mb, microarray analysis achieves detection of genomic imbalances with a diagnostic resolution of 50 to 100 kb.
Are you insured in Germany? Our colleagues at the Zentrum für Humangenetik Tübingen will gladly support you!
What We Offer with This Service
Our Promise to You
Indication of Array CGH
For many diagnostic questions, array CGH has become the “first-line” method to clarify the cause. In particular, the use of array CGH is indicated in the following cases:
- unclear mental retardation (IQ < 70)
- suspicion of changes from the autism spectrum
- functional disorders or malformations affecting the brain
- dysmorphic abnormalities
- congenital malformations of unclear etiology/li>
- prenatal ultrasound abnormalities
- growth retardation or abnormalities (pre- or postnatal)
or
- for a more precise characterization of cytogenetically proven aberrations
- for the verification of aberrations that appear balanced in clinically conspicuous patients
- for characterization of genomic rearrangements
- as a complementary investigation to molecular genetic methods (e. g., further characterization of MLPA findings; validation of NGS results, if applicable)
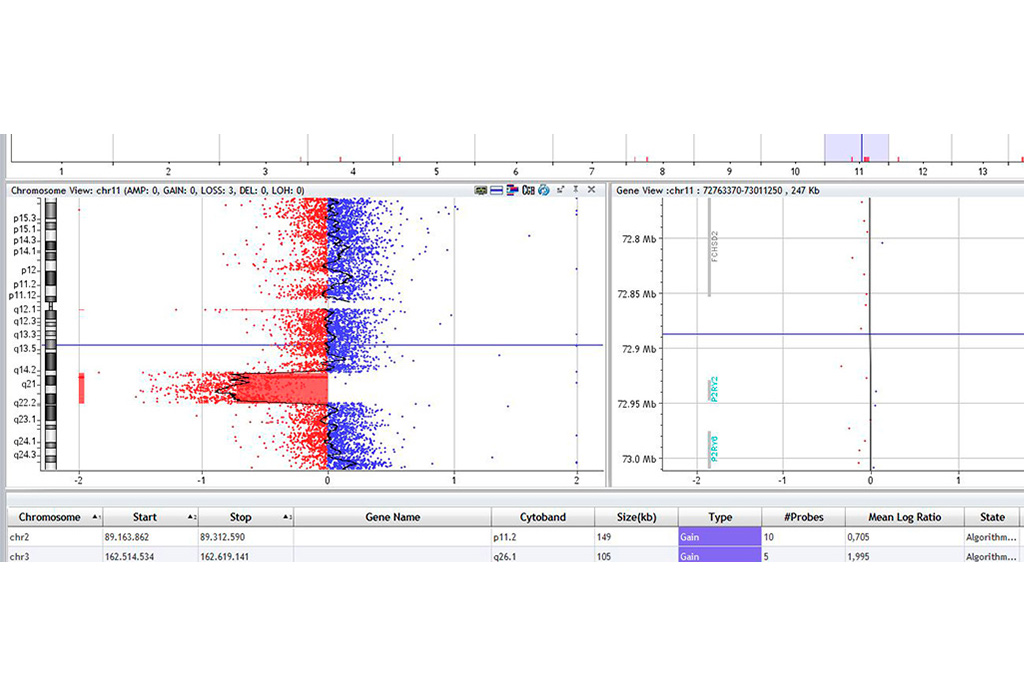
Sample Report
General Information
Material
- 1 ml – 2 ml EDTA blood (recommended sample type) or 1 µg – 2 µg of genomic DNA
- order form
Here you can find more information on how to ship your sample safely.
Turnaround Time
- processing time: 4-6 weeks
What Is an Array CGH?
Array CGH analysis is a molecular genetic method that can be used to detect small gains or losses in chromosomal material below the detection limit of conventional chromosomal analysis. In array-based comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), patient DNA samples and a reference DNA are labeled with different fluorescent dyes and cohybridized on a carrier chip with immobilized DNA fragments (probes). These probes cover the human genome as uniformly as possible. Numerical changes result in a color shift of the fluorescence signal for the individual probes. These signals are detected by a laser scanner and assigned to the respective chromosomal region, and displayed using appropriate software (“molecular karyotyping”).
At CeGaT, all available array formats from Agilent can be processed, analyzed, and diagnosed. In routine, we use the Agilent 180K array with a diagnostic resolution of ≥ 50kb.
After the consultation, it is also possible to analyze individual high-resolution arrays.
Precise Results through Array CGH Analysis
By detecting microdeletions and microduplications in a patient’s genome, array CGH analysis can detect significantly smaller abnormalities than conventional chromosome analysis. Conventional chromosome analysis identifies a structural genomic alteration in only about 3%–4% of the patients with developmental delays examined. With genome-wide analysis, array CGH analysis allows the detection of causative alterations in up to 15% of patients. Array CGH analysis can resolve unclear cases of mental retardation or rare syndromic conditions. In addition, losses or gains identified by chromosomal analysis can be characterized more precisely.
Contact Us
Do you have a question, or are you interested in our service?
Diagnostic Support
We will assist you in selecting the diagnostic strategy – for each patient.